Uses for a queue
#
What is a Queue?
A queue is a dynamic data structure that allows for the removal of elements and the insertion of new objects. More specifically, a queue is a structure that follows the rule of operation where whenever there is a removal, the element removed is the one that has been in the structure the longest. Queues follow the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle, where the first element added is the first to be removed. This is useful for many applications in distributed systems, where the order of operations is important.
#
Use Case
Imagine we have a user API.
With this API, we can create users, update them, delete them, and receive a response for these operations, send an email to the user, and make a request to another API. In this scenario, if an email fails to send, the entire request will fail, and another request must be sent to achieve a successful response.
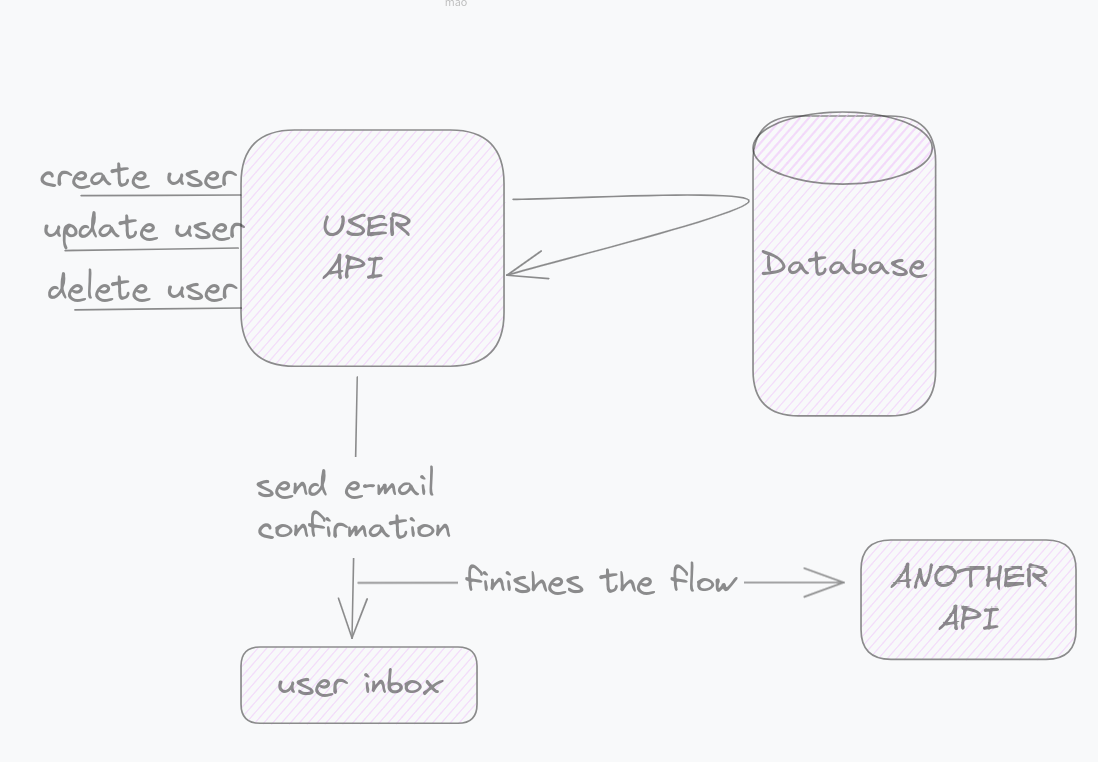
However, it doesn’t have to be this way. Sending an email and making the request to another API in this flow is not crucial and can be done asynchronously later.
#
Introducing the Concept of a Queue
Here enters the concept of a queue. Instead of doing all these operations synchronously, we can do only the crucial ones synchronously and the rest asynchronously by adding to the queue what can be done later.
To make this work, it’s necessary to have a consumer service that will be listening to the queue and will do something with the information in the queue, like sending an email.
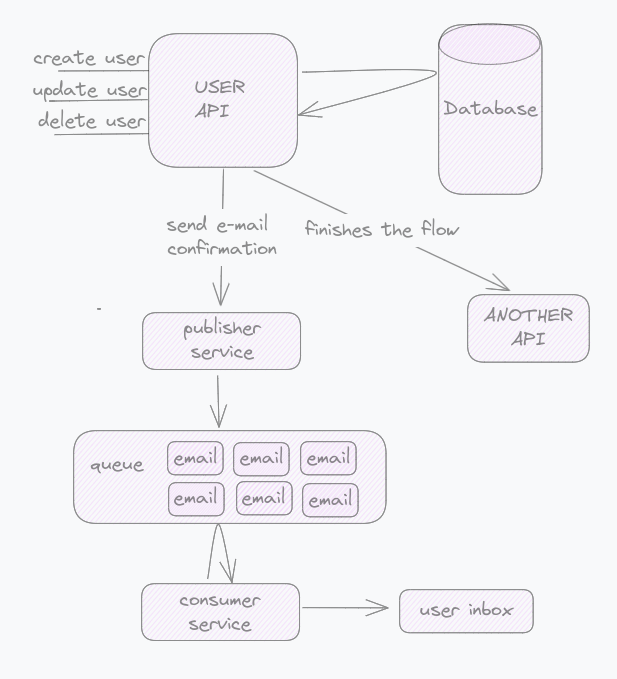
This makes your system more resilient. If something fails in the processing, the message goes back to the queue and will be reprocessed later.
#
Benefits of Using Queues
- Resilience: If a system component fails, the message can be reprocessed.
- Scalability: Publishers and consumers can be scaled independently.
- Decoupling: Reduces direct dependency between system components, allowing for greater flexibility and maintenance.
- Load Management: Queues allow the system to handle load spikes by distributing processing over time.
- Priority: Messages can be prioritized to ensure the most important ones are processed first.
#
Tools
##
AWS SQS (Simple Queue Service)
AWS SQS is a fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. With SQS, you can send, store, and receive messages between software components.
##
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is one of the most widely deployed open-source message brokers, used both in the cloud and on-premises. It’s a reliable messaging middleware that can be used for message queuing, message routing, load balancing, and more.
##
Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform. It’s used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications, offering high throughput, low latency, and message durability.
#
Conclusion
Using queues can make your system more robust and efficient, allowing non-crucial tasks to be processed asynchronously. This improves the resilience and scalability of the system, ensuring that failures in secondary operations do not affect the user experience. Additionally, with tools like AWS SQS, RabbitMQ, and Apache Kafka, implementing queues is accessible and powerful.